

- Home
- Company Information
- Sustainability
- Environment
- Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations
The Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) was established by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) at the request of the G20 to examine how to disclose climate-related risks and opportunities, and how financial institutions should respond to the disclosures. The TCFD recommends that all companies disclose climate-related information in line with the four thematic areas: governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets. We will thus disclose our information in accordance with the four disclosure recommendations.
Governance
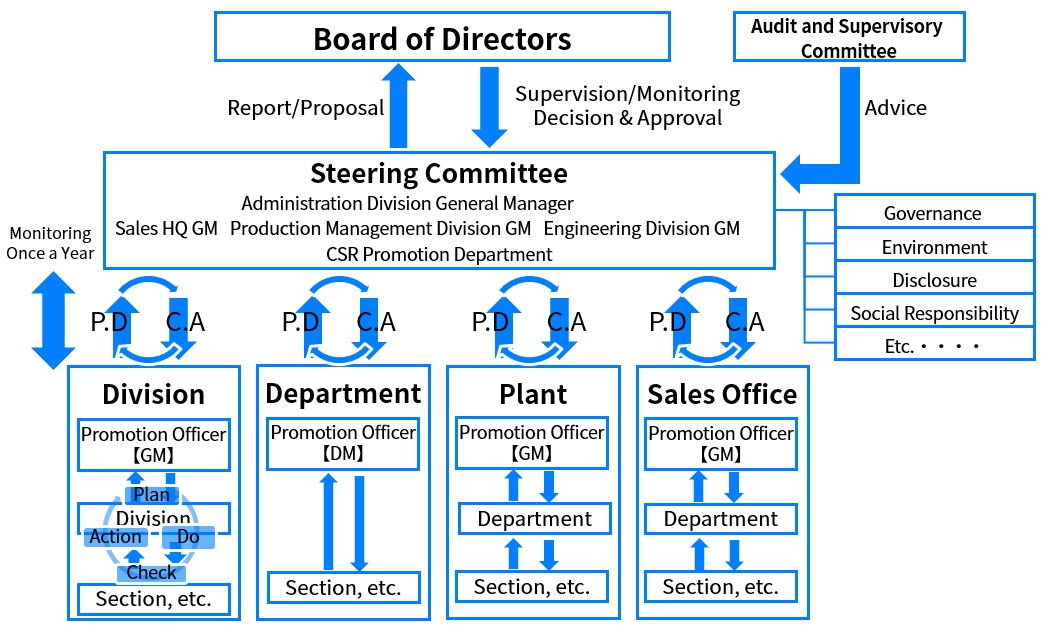
- ・The Steering Committee is organized under the guidance and supervision of the Board of Directors. The Director and General Manager of the Administration Division serves as the Head of the Committee. The General Managers of the divisions have a key role in overseeing overall risk management policies.
- ・Four times a year, the General Managers of the divisions examine climate-related risks and opportunities for our business, which arise from mid- to long-term climate change impacts, and take necessary measures in cooperation with the departments involved in the risk management.
- ・The results will be reported to the Steering Committee, and any matters that may have a significant impact will be reported to and submitted for discussion at the Board of Directors meeting twice a year.
- ・The Audit and Supervisory Committee provides advices to the Steering Committee as appropriate.
〈Governance and Risk Management Organization Chart〉
Strategy
(1) Business Strategy
We assessed where and how the climate-related risks and opportunities have influenced our business. The risks and opportunities refer to “transition” risks and opportunities that arise from changes in social demands such as policies and regulations, or to “physical” risks that arise from extreme weather events. Each risk category specifies the items that could have an impact on the company’s profit and loss.
We performed scenario analysis by using the “science-based scenarios” piloted by the International Energy Agency (IEA) and other organizations to assess where and how our business would be influenced. At this time, the scenario analysis coverage is the entire supply chain of the Group, which includes the purchasing, development, manufacturing, sales, and disposal of products and services. We used two scenarios, the IEA 4°C scenario and 1.5°C scenario, to investigate and assess the climate change impacts in 2030.
We aim to achieve the “net zero” emissions from electricity by 2025 and to reach carbon neutrality by 2050. As a result of calculating climate-related impacts on our group business by using the public climate scenarios, we have been playing a part in reducing global CO2 emissions by focusing our business on xEVs to lower carbon emissions as well as by reducing carbon footprint of our own business.
When it comes to specific measures to reduce emissions, we are committed to reducing energy consumption to mitigate negative impacts, replacing production equipment with energy-efficient appliances to improve energy use intensity, and focusing on xEV-related businesses and local production for local consumption to drive positive impacts. Besides, we have been using recycled materials for our products and improving production efficiency through reassessing the manufacturing processes.
(2) Analysis of climate-related impacts on our business and finance
Under the 4°C scenario
The 4°C scenario assumes that, if any actions were not taken to respond to climate change, the average global temperature would increase by approximately 4°C by the end of the 21st century compared to the level of pre-industrial times. Whereas the level of physical climate risks such as worsening extreme weather events and sea level rise would increase, restrictions imposed on future business and consumption activities would be less stringent than they are today.
Looking at the business impact under the 4°C scenario, we assume that climate change, such as warmer temperatures, would lead to increased health risks for employees working in areas where we run our business, and then to higher response costs. Besides, supply-chain disruptions caused by extreme weather events could cause delays or suspension in material procurement, which would make it harder for us to continue our business.
The profit impact for FY2029 would be a decrease of approximately 690 million yen, premising that we will meet our long-term vision target of net sales of 100 billion yen by FY2029. (Note)
Under the 1.5°C Scenario
The 1.5°C scenario assumes that, if global efforts to reach carbon neutrality were accelerated, the average global temperature rise would be limited to about 1.5°C by the end of the 21st century compared to the level of pre-industrial times. While physical climate risks would not increase, restrictions on business and consumption activities would be more tightened by imposing taxation and legal regulations.
When it comes to the business impact under the 1.5°C scenario, we anticipate that additional costs would be generated by rising energy prices, implemented carbon taxes and the expansion of the emissions trading scheme if global activities are intensified to achieve carbon neutrality, as well as that global xEV sales growth would cause the sharp rise in metal prices. Meanwhile, business opportunities for our products would increase as a result of growing demand for low-carbon technologies, including renewable energy and xEVs to build a zero-carbon society.
The profit impact for FY2029 would be a decrease of approximately 950 million yen, promising that global xEV growth will enable us to meet our long-term vision goal of 120 billion yen in net sales in FY2029. (Note)
Note: An estimated impact on gross profit, compared to the FY2020 level (unit: billions of yen)
| Under the 4°C Scenario | Under the 1.5°C Scenario | |
|---|---|---|
| Impact of electricity prices | – | -0.2 |
| Impact of fuel car market decline and xEV market expansion | – | 65.5 |
| Impact on raw material cost | – | -70.6 |
| Loss due to worsened extreme weather events and changes in rainfall and weather patterns. | -0.67 | -0.38 |
| Other | -0.2 | -0.3 |
| Total | -6.9 | -9.5 |
(Estimated value as of March 2024)
Risk Category and Impact Analysis
| Risk Item | Business Impact | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Sub-category | Further Sub category | Timeline |
Index |
Risk | Opportunity | Impact Level |
| Transition | Policy and Regulation |
Carbon Pricing (Carbon Tax) |
Mid- Long Term |
Revenue and Costs |
|
|
Major |
| Emissions Trading |
Short-Long Term | Revenue and Costs |
|
|
Major | ||
| Response to GHG Emissions Limit | Short-Long Term | Revenue and Costs |
|
|
Major | ||
| Market | Changes in Energy Cost |
Mid- Long Term |
Revenue and Costs |
|
|
Major | |
| Changes in Customer Behavior |
Mid- Long Term |
Revenue and Costs |
|
|
Major | ||
| Physics | Acute | Worsening Extreme Whether Events (Typhoon, HeavyRain, Debris Flow and Storm Surge) |
Short Term | Revenue and Costs |
|
|
Major |
| Chronic | Rise in Average Temperature | Mid- Long Term |
Revenue and Costs |
|
|
Moderate | |
(Note)
- 1 Transition risks and opportunities (chances) refer to risks and opportunities that have an impact on corporate revenue and financial conditions, which arise from policies, regulations, legal systems, as well as from changes in social demands and business environment associated with them.
- 2 Physical risks and opportunities refer to the risks and opportunities that a company’s revenue and financial status are affected by physical phenomena, including extreme weather events such as more intensified typhoons mainly due to increasing greenhouse gas emissions and rise in average global temperature and sea level.
Risk Management
- ・Our climate-related risks are identified, evaluated and managed at the Steering Committee.
- ・Based on the results of risk assessments conducted by each division, the need for measures and priorities are considered and reported to the Steering Committee.
- ・As a result of the risk assessments, cases and responses that may have a significant business impact are reported to the Board of Directors, which makes necessary decisions on them after receiving a request for decision.
- ・Each division creates and implements a risk mitigation plan under the instructions and guidance of the Board of Directors as well as the Steering Committee.
- ・The Company has also developed an environmental management system based on ISO 14001. The climate-related risk management includes the monitoring of risks such as compliance risk, which is based on the ISO management system.
Metrics and Targets
As the following targets are set for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, we are working on solar system installation, plant automation, energy-saving practices through production efficiency improvement by increasing the efficiency of plating lines, and switchover to renewable energy. In the future, we will also respond to carbon pricing.
〈Reduction target〉
- ・CO2 emissions from electricity: virtually 100% reduction by 2025
- ・GHG (Scope 1-3) emissions: Achieve carbon neutrality by 2050
〈Sustainable Development Goal〉
・Numerical Target
| Item | Year | Target | Targets for the year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electricity Consumption intensity (Electricity Consumption/Net Sales at Plant) |
2030 | VS. FY2020 -30% |
FY2020 -3.5%/year |
| Use of EVs as company cars | 2030 | 100% | – |
| Tracking of suppliers’ SCOPE1~3 emissions(CO2 emissions tracking) |
2030 | 80% of Procurement cost |
FY2022:15%、 After 2023: +10%/year |
・Other Goals
- ・ Product development for contributing to society’s carbon neutrality and review of power usage for supporting technological development, including chemical recycling, etc.
- ・Choosing companies that have low CO2 emissions and renewable energy sources
For ESG data such as the company’s electricity consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, see this page.

